Ozone O3
Sources
Ozone is not emitted into the air but formed from oxygen and NO2 in the presence of sunlight and volatile organic carbon (VOC). Both VOC and NO2 - as a part of NOx - come mostly from motor vehicles and stationary sources. They can be transported over great distances and result in high ozone concentrations over large regions.
Health effects
Ozone can cause health effects even at relatively low concentrations. People particularily sensitive to ozone are children, people with lung disease, older adults, and people who are work outdoor. For them the risk of health problems including chest pain, coughing, throat irritation, and congestion is higher. Ozone can furthermore worsen bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma. Repeated exposure may permanently scar lung tissue, reduce lung function and inflame the linings of the lung.
Environmental impacts
Plants absorb gaseous ozone through the stomata in the leaf surface. The leaf organs can be damaged. Ozone is responsible for agricultural crop yield loss and the damage of forest ecosystems in large areas.
O3 concentrations
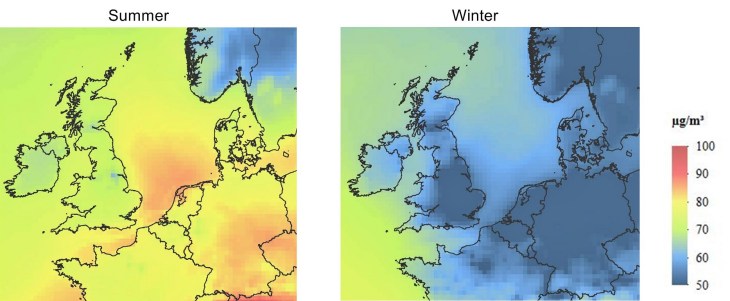
The O3 concentrations are higher in summer, as the formation process is highly dependent on UV-radiation. It can be seen that a formation over the main shipping route is taking place as the concentration reaches between 80 and 90 µg/m3.
Relative contribution of ships to the O3 concentration
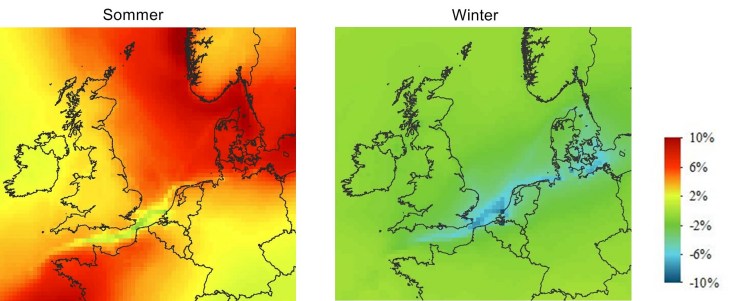
Shipping causes additionally 7 µg/m3 of ozone (summer average value) in large parts of the North Sea and Denmark. Where NOx concentration is high, like in the English Channel, a small increase in ozone is found.
Scenario No ECA: O3 Concentration Change

The effect of ozone destruction by additional NOx emissions under low VOC (volatile organic carbon) conditions can be clearly seen in scenario No ECA. These conditions lead to a reduction of the contribution of ships to the ozone concentrations of up to 80% in the Channel.
Scenario ECA SCR 21: O3 Concentration Change
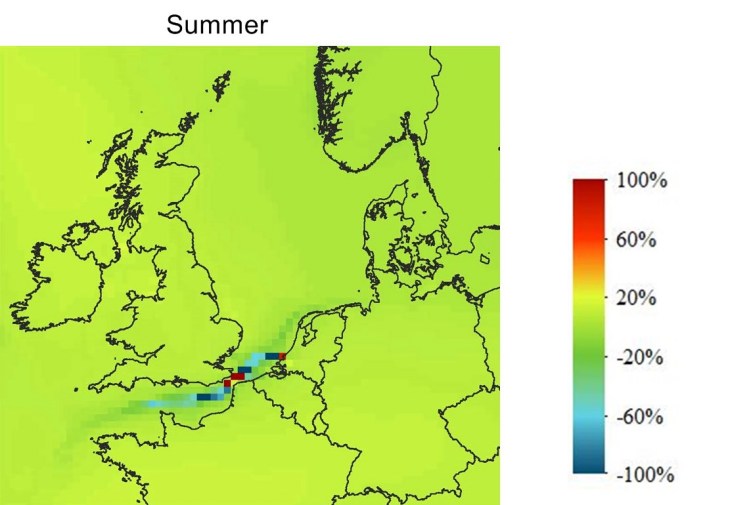
This scenario contains higher NOx values leading to a decrease of ozone in the Channel and higher values over Central Europe.
Scenario ECA SCR 16: O3 Concentration Change
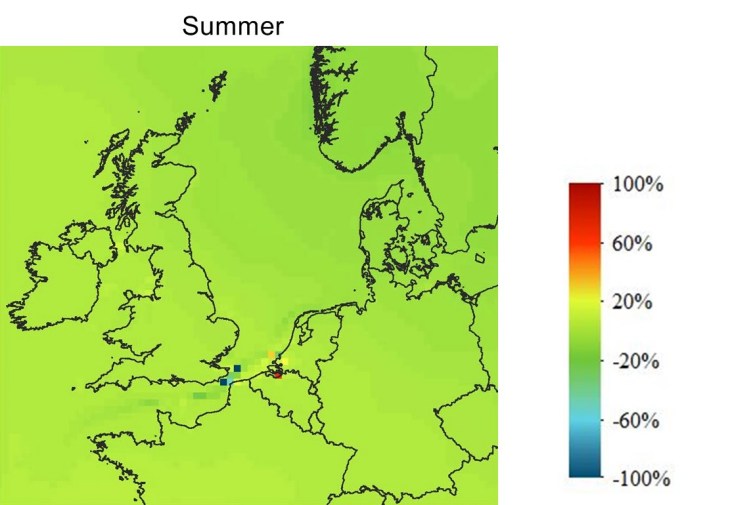
The ECA SCR 16 scenario shows a lower shipping contribution to ozone concentration and an unchanged situation in the South West.
Scenario ECA opt: O3 Concentration Change
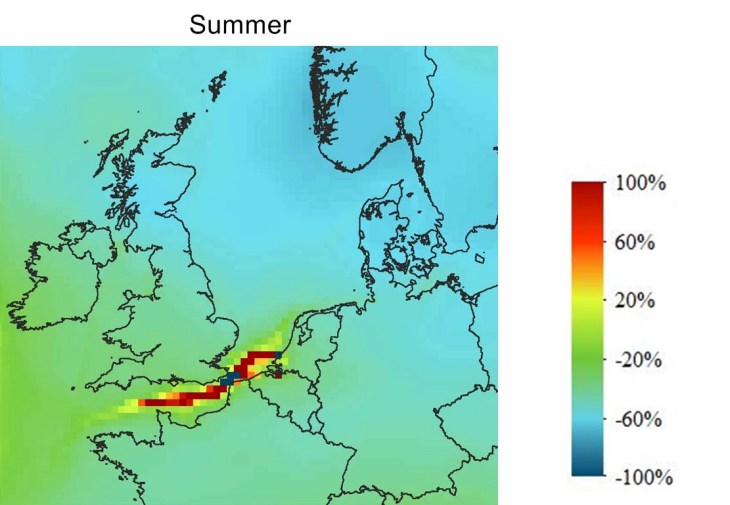
In this scenario the contribution of ships to the ozone concentration is significantly reduced over the whole North Sea by 30%-60%. The Channel is the only region where a significant increase of 80% or higher was found. The reason is that depending on the presence other reactive substances in the atmosphere NOx can both trigger the production and destruction of ozone.
